By Austin OKERE
On May 04, 2020, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), in a report about poverty and inequality from September 2018 to October 2019 in Nigeria, said 40 per cent of people in the continent’s most populous country lived below its poverty line of 137, 430 naira ($381.75) a year. It said that represents 82.9 million people.
I had written this article about four years ago on Nov 15, 2016, about how society today is split more along the lines of those who are included and those left behind. This is even truer today with Businesses and Education moving Online due to the COVID-19 induced Social Distancing. How can we ensure that nobody is left behind?
While society in the past was split between the haves and have nots, society today is split more along the lines of those who are included and those left behind. This inequality is most heavily felt in emerging markets, where 80% of the world resides.
India As An Example
Take for instance fast developing India, while globalisation has significantly increased GDP, it has also expanded the already wide chasm between the rich minority and poor majority. For instance, seven companies on Fortune’s 2016 Unicorn List are in India, mostly in the e-commerce sector. That’s more than South Korea, the Netherlands and Canada combined. However, the 12.5m employed directly and indirectly by the ICT sector and contributing 25% of India’s export revenue, accounts for only 2.5% of the national labour force.
The bottom line is that India is an agrarian society with more than half the population engaged in agriculture and allied industry. By cutting subsidy on irrigation and other rural needs, and switching farm output from food crops to fertiliser intensive cash crops, the poor have gotten poorer. On the other end of the chasm, the number of dollar billionaires in India has jumped to 110 in 2015; the third-largest after the US and China, while dollar millionaires have crossed the 250,000 marks. This is what the Canadian political philosopher, Crawford Macpherson describes as the ethic of possessive individualism.
Growth Without Prosperity, Youths Most Impacted
In his book, Innovation and Entrepreneurship, famed author, Peter Drucker wrote about an entrepreneurial society and its impact on economic development. An entrepreneurial society is one that is either prosperous or on a path to prosperity; different from mere growth. Economies can grow without becoming prosperous. We saw this happen in the 2000s when many African economies, such as Nigeria, Angola, and Equatorial Guinea, were the fastest growing in the world but failed to create prosperity for millions of their citizens.
A close examination of those left behind shows that they are mostly the youth of our society. For example, while the unemployment/underemployed rate in Nigeria is 32.6%, the rate among the age bracket of 15-24 years is as high as 58.3%. The sheer size of unemployed youths is surely a time bomb waiting to explode, as they are left to be seduced by terrorist ideals or other antisocial proclivities out of desperation.
Ascension Of The Right Wing
The surge in the popularity of right-wing politicians across Europe and the rest of the world is a testimony to the exasperation of the silent majority of society who feel left behind, as was manifest in the recent unexpected emergence of Donald Trump as President-elect of America. The Brexit vote in the UK highlights the division of the demography into those who belong; mostly the elite, who voted to remain and those left behind, who largely voted to leave.
The view widely held is that while globalization has brought awareness to premium products and urban lifestyles across boundaries, it has robbed nationals of jobs, which are now being shipped to other regions with more competitive production costs. It is also perceived that jobs at home are fast being snapped up by immigrants who are either more qualified or willing to work for less pay. The vote against globalisation and liberalisation in favour of nationalistic border controls is more a protest against immigration than any firm convictions of its demerits.
Non-Consumption Could Be The Root Cause
Many of those in a society stuck at the wrong end of the Gini-coefficient is majorly locked out of the ‘consumption pool’ for a variety of reasons; including affordability, availability and awareness.
According to Efosa Ojomo, a research fellow at the Clayton Christensen Institute for Disruptive Innovation, the way we define competition, and the method employed by companies to assess the competitive landscape leaves out the most important competitor of all – non-consumption. And nowhere is this feisty competitor more prominent than in emerging markets.
While companies compete for the few people in the consumption pool, their fiercest competition is the huge segment of society that is not consuming. Finding ways of including this large demography will not only boost production, sales and distribution but will also provide additional jobs to meet the increased demand. This sets off a self-sustaining cycle of growth and further inclusiveness.
According to market intelligence firm, Euromonitor, in 2015 only 2.5 per cent of households in emerging markets had access to air-conditioners, while just 19 per cent had access to refrigerators and barely 9 per cent had access to cars. Compare these numbers with those in the United States, where 83.4 per cent of households have air-conditioners, 99.9 per cent have refrigerators, and 86.5 per cent have automobiles.
Market-Creating Innovation To The Rescue
Entrepreneurs, investors, and managers can invest in what Harvard Business School Professor Clayton Christensen calls ‘market-creating innovation’ to transform complicated and expensive products into simpler and less expensive products, making them accessible to significantly more people in society. Market-creating innovations pull people from non-consumption into the consumption pool. Companies that engage in these types of innovations are the engines of economic growth in an economy. It is through market-creating innovations that the other types of innovation such as potential innovation and efficiency innovation are birthed.
A perfect example of a market-creating innovation is Henry Ford’s Model T car. Henry Ford was able to manufacture a car that was inexpensive enough for an American with a modest income to purchase. He also made the car easier to drive so that owners would not have to hire a driver or need special expertise. Some of Ford’s innovations were the assembly line which reduced the Model T chassis assembly from 12.5 hours to 1.5 hours. Ford passed on the cost savings to the new class of consumers of automobiles such that by 1925 the price of his car had plummeted from $825 to $260.
The Modern Age Of Platforms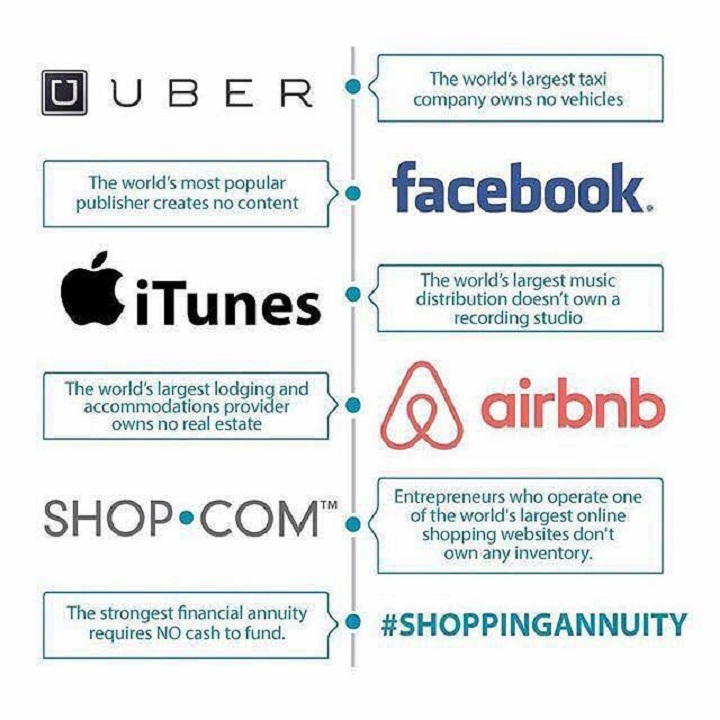
Enter the modern age of Platforms such as Facebook, Google, Amazon, Uber and Airbnb. There is hardly an area of economic and social interaction these days that is left untouched by these Platforms in some way. Two major areas in which the Platform Czars have riled the establishment are in transportation and hospitality; the major ‘culprits’ being Travis Kalanick of UBER and Brain Chesky of Airbnb.
UBER, until recently a relatively unknown company out of Silicon Valley in California, employs 327,000 drivers today and is adding an average of 50,000 drivers every month. This transport services disrupter is now valued at $62.5b and operates in many major cities across the globe. Airbnb, a previously obscure company with similar roots, has over 2.8m accommodation on her platform and is now valued at $30b. These Platforms provide a means of significantly extending services at low-cost efficiencies, and as a result draw many people into the consumption pool, while also creating many jobs along the value chain which would otherwise simply not exist.
A major concern of the new Platform Economy, however, is data security and confidentiality. The bigger problem is about governments getting interested wherever there are large amounts of data, and seeking to gain access to it, perhaps for tax purposes, security or otherwise. How do the Platforms, which typically generate tons of customer data, handle this dilemma?
The Education Bottleneck
Urbanisation and inclusiveness will put a strain on the current education structure as a result of unprecedented demand for knowledge workers. This makes education another area where there is a need to reach far more than our traditional schools can cater for. Here again, leveraging on online learning Platforms to provide Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) are coming to the rescue. In the past, if you wanted to get a qualification, or even simply learn something new, you would sign up for a course at a bricks-and-mortar institution, pays any relevant fees, and then physically attend class. That was until the online learning revolution started.
According to Zi Hu, MED candidate, Columbia University, last year the e-learning market was worth an enormous $166.5 billion and estimated to reach $255 billion by 2017. Its growing financial value is matched only by the swelling numbers of students choosing to follow an online course, making online learning seem like the future of education. Instead of worrying whether or not online education can ever be as good as more traditional formats, perhaps we should instead focus on how we can use it to deliver quality education for people all over the world, particularly the poor and underserved.
Broadband And Smartphones As Platform Vehicles
The ubiquity of broadband and the proliferation of smartphones has extended the life of Platforms and made services that were hitherto unavailable to a large section of the population possible. This heralds an era of unprecedented inclusiveness. For instance, MPESA in Kenya has made it possible for a large swathe of the population to gain financial inclusion by providing the opportunity to transact financial services vide your mobile phone on a continent where typically 70% of the population is unbanked. Similar applications have metamorphosed across Africa.
Regulatory Challenges
While Platforms will bring inclusiveness and bring a lot of people into the consumption pool, there are major regulatory challenges that have to be surmounted as a result of issues that were not foreseen when the governing statutes and regulations were enacted. To fill the regulatory gaps these Platform behemoths have resorted to what could be referred to as spontaneous deregulation, which has arisen as a result of Platform disrupters ignoring laws and regulations that appear to preclude their business model.
Believing in the efficacy of their utility model and its appeal to a pent up global demand, these disrupters seem to see many rules and regulations as belonging to the past and impractical for today’s innovative clime. They, therefore, simply ignore them, opting for their own version of self-regulation, usually based on a mutual rating system between service providers and consumers.
A bigger dilemma perhaps is the placement of regulation. For instance, who should regulate the plethora of Fintech companies springing up globally and providing Platforms for financial inclusion; should it be Central Banks or the Communications Commissions? The jury is still out on this. Another major worry is the issue of the Platform provider having an undue advantage by also being a player on his Platform. This makes him the judge and jury in his own case.
A Case For Platforms, And Their Expansion
A big plus for platforms, albeit more out of serendipity than design, is the lowering of the carbon footprint, a major consideration of both the millennium and sustainable development goals. With all the perceived drawbacks of Platforms, they will significantly help in bringing more people into inclusiveness, who otherwise would have been left behind.
I believe that Platforms will, in the long run, contribute more towards saving society, especially if extended beyond their current technology boundaries into other non-consumption realms to maximise their impact towards achieving a more equitable society.
Austin Okere is the Founder of CWG Plc, the largest ICT Company on the Nigerian Stock Exchange & Entrepreneur in Residence at CBS, New York. Austin also serves on the Advisory Board of the Global Business School Network, and on the World Economic Forum Global Agenda Council on Innovation and Intrapreneurship. Austin now runs the Ausso Leadership Academy focused on Business and Entrepreneurial Mentorship

