By Austin OKERE
“Customers besiege banks on the first day of the partial lifting of COVID-19 lockdown: As early as 8 am, bank premises were already full of people seeking to gain entrance into the banking halls for one transaction or the other. And by 11 am, Twitter was filled with so many posts warning Nigerians about the risks of visiting any bank branch due to the mammoth crowd.” This was Dateline May 04, 2020, on Nairametrics.com. Other blogs had similar screaming headlines.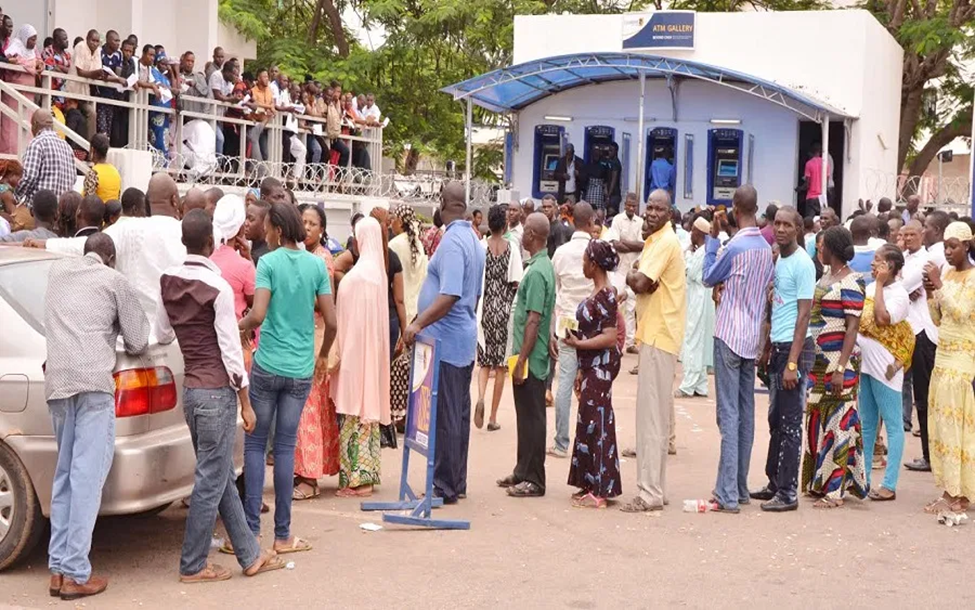
I wrote this article three years ago on May 04, 2017, when Blockchain and Fintechs finally seemed to be gaining traction in filling the gaps left by traditional banks – and surprised that we are still where we are even today. What will we learn from this, and how will we be better prepared not to be caught desperately unawares again?
Even though cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin tend to steal the limelight, it is their underlying blockchain technology that is proving to be of practical benefit. This technology, which goes beyond the financial application, is expected to disrupt global supply chains by boosting transaction speed across borders and improving transparency.
Essentially, the blockchain is a shared virtual public ledger where encrypted transactions are confirmed by outside parties. Confirmed transactions are placed in a “block” and added to the chain, hence the name Blockchain. It is this technology that Fintechs are leveraging to disrupt the traditional banks
Here in Nigeria, blockchain can help to unlock the immense capital locked in Land Assets that are not enumerated because of an antiquated system of land administrated, which is very ripe for disruption.
The most disruptive application of Blockchain Technology, however, is in the Financial Sector; and this will form the focus of my discourse. The consistent complaint about banks has reached a crescendo in recent years. Is this justified?
Should Banks be changing?
Dateline, May 04, 2020, on Niarametrics.com After centuries of conservatism in receiving deposits and making loans, there are two main issues stirring the yearning for change:
- The first being that it is a very difficult Club to join as a customer, and hence the large population of unbanked adults.
- Secondly, even for the members of this elite club, the relationship is acutely skewed in favour of the banks
They have carried on as protected monopolies with no serious challenge or competition, resulting in very little innovation over the decades.
The biggest threat to the banks has been precisely their seeming success. Centuries of relatively significant higher returns, even during economic downturns that adversely affect the real sectors, has engendered an attitude of invincibility and pomposity, characterized by a loss of touch with their customers.
Considered too big to fail, they take it for granted that they will be bailed out with taxpayers’ money in the event of any missteps – this is a perfect set-up for disruption.
Fintech – the new kid on the block
Today, there has emerged a powerful force of the challenge from Financial Technology companies or FINTECHs, as they are more popularly referred to. The promise of Fintech is great. It is shaking up a stodgy banking system and helping to build a more efficient one, especially for consumers and small businesses.
Emerging Markets showing the way in Fintech
For years, emerging economies have looked up to developed countries for ideas about how to manage their financial systems. When it comes to Fintech though, the rest of the world will be studying the experience of the emerging markets, embodied by the widely successful MPESA mobile money system, championed by Safaricom in Kenya.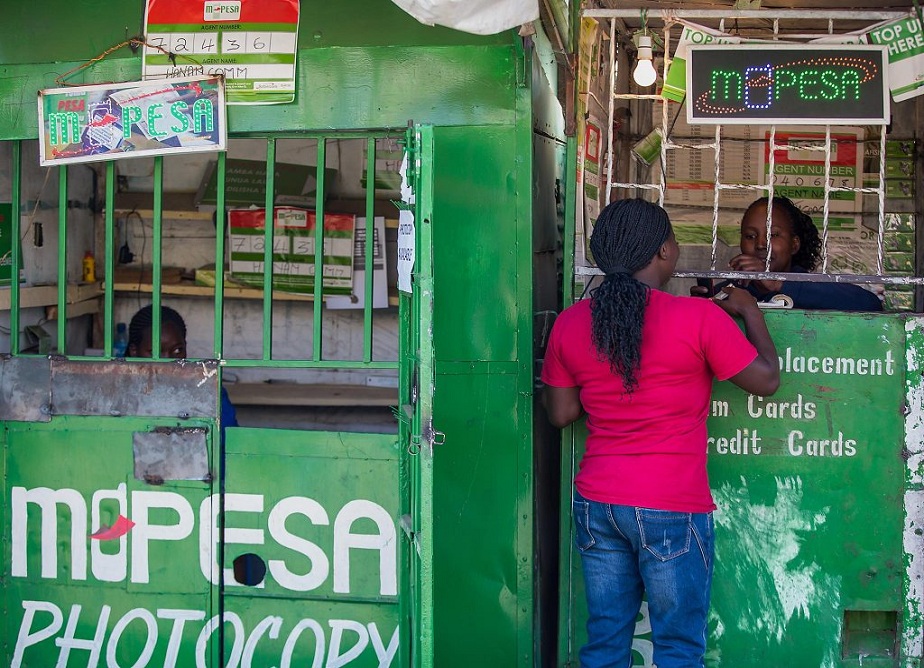
MPESA has made it possible for a large swathe of the population to gain financial inclusion by providing the opportunity to transact financial services via your mobile phone, on a continent where typically 70% of the population is unbanked.
MPESA today has more than 60% of Kenya’s 33 million mobile users and in 2015 transacted $28m on her platform. Similar applications have metamorphosed across Africa, and Mobile Money services are today generating 6.7% of Africa’s GDP.
Nigeria is no exception with Fintechs such as Interswitch, CWG, Paystack and Flutterwave holding sway. Take, for instance, Diamond bank with 7m accounts after 23 years was able to add an additional 6m accounts in just one year after the launch of the Diamond Yello Account in collaboration with CWG and MTN.
China is the undisputed World leader in Fintech
By just about any measure of size, China is the world’s leader in Fintech. It is by far the biggest market for digital payments, accounting for half of the global market, according to the Economist Magazine. A ranking of the world’s most innovative Fintech firms gave Chinese companies four of the five top slots in 2016. The largest Chinese Fintech company, Ant Financial, has been valued at about $60b, at par with UBS which is Switzerland’s biggest bank.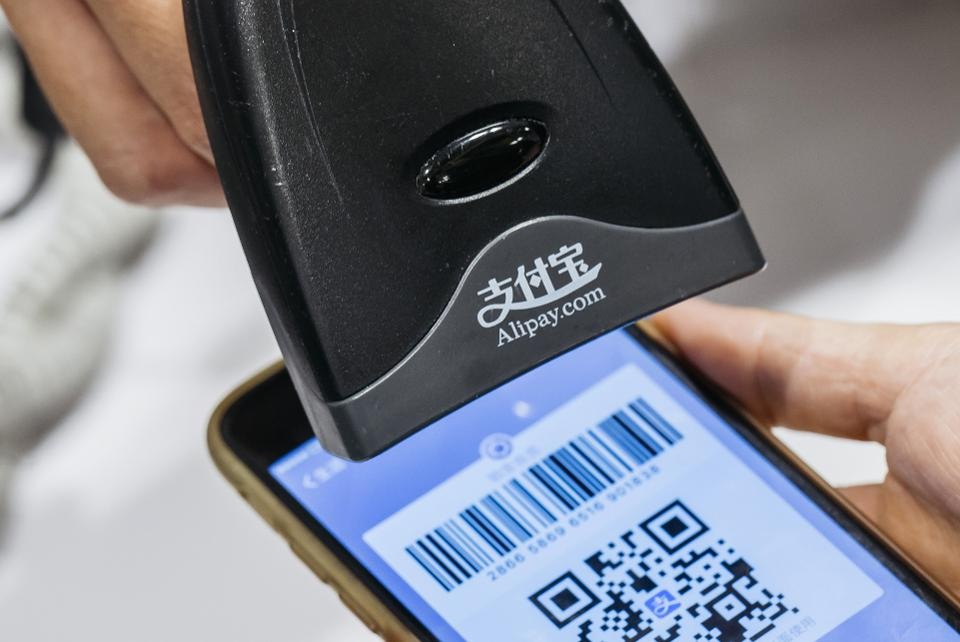
Today, digital payments account for nearly two-thirds of non-cash payments in China, far surpassing debit and credit cards. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) lenders in China grew from 214 to over 3,000 in 2015, and P2P loans increased 28-fold from 30b yuan in 2014 to 850b yuan in 2016. This shows what is possible in Nigeria.
Austin’s Five Forces Model and the future of Banking
In the face of the fierce challenge facing banks, I developed a model for analyzing the future of banking called the Austin’s Five Forces Model. There are indeed five major forces at play here:
- The banks – traditional and established, best with cash and ancillary instruments
- Fintechs – the new kid on the block, disrupter, mostly telecom roots, best with digital currencies and mobile services
- Regulators – Central Banks, regulating traditional banks; and Communication Commissions, responsible for telecoms regulation (and thus Fintechs)
- Currencies – traditional, such as cash and cheques; or Digital, including Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies
- Customers and the weight of their new-found voice. Typically, they clamour for whatever will give them convenience, security and lower costs.
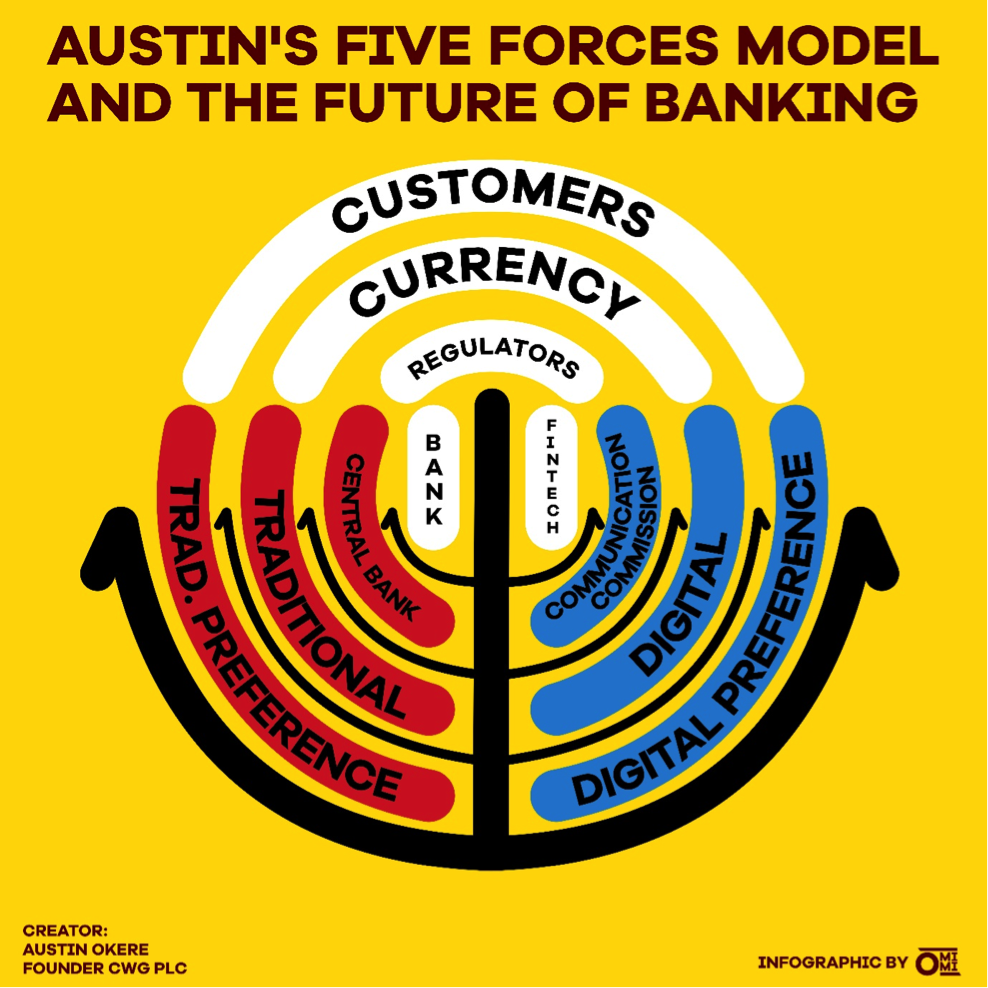
Customers are the most significant force and represented by the outermost sector of the concentric circles. As they tend more towards a preference for digital currencies, the Fintechs will tend to assume a more prominent role in the new face of banking, and the Regulatory regime will inadvertently tend towards the Communication Commissions under whose purview the Fintechs fall.
This will introduce a regulatory imbroglio, as future ‘Huge Banks’ may fall outside the regulatory ambit of Central Banks as seems to be the case with the MPESA.
Safaricom, the telecoms promoter of MPESA ironically falls under the regulation of the Communications Authority of Kenya rather than the Kenyan Central Bank.
If the customers, however, maintain a strong appetite for traditional instruments of financial transactions such as notes & coins, cheques etc. then the current status quo will remain. The face of banking will thus be more of the same, and the regulatory authority will continue to be Central Banks. Between these two positions may be many variants, depending on the appetite and preferences of customers, and the pace at which they are willing to embrace change.
Retailers are jumping into Financial Services
Fintechs are not the only ones challenging traditional banks for turf. Retailers are also jumping into the financial services fray. For instance, Amazon has launched Amazon Cash, a way to shop its site without a bank card. This product is meant to appeal to the those who get paid in cash, don’t have a bank account or debit card, and who don’t use credit cards.
Google is also rolling out a new integration on mobile called Google Tez, which allows audio QR Codes and thus opens the door for more basic phones other than smartphones. Users of the Gmail app on Android will be able to send or request money with anyone, including those who don’t have a Gmail address, with just a tap.
Banking is going Mobile
In most emerging markets and developing countries, the current formal financial system only reaches a minority of the working-age adult population. Smallholder farmers, self-employed households, and micro-entrepreneurs have to rely on the age-old informal financial mechanisms such as rotating savings clubs (Isusu or Ajoo). These mechanisms can be unreliable and very expensive.
In Nigeria, for instance, 84.6m people, accounting for 47% of the population are unbanked. In sharp contrast, mobile phone penetration is very high at 94.5 per cent; a perfect set-up for the Fintechs to exploit in their mobile dominated financial services offering.
The digitization of retail payment systems and financial services has become an important economic development priority. It offers the prospect of reaching far more people at far lower costs with the broader range of financial services they need to build resilience and capture opportunities. This speaks to inclusiveness.
What will be the scale of change of Blockchain technology?
The changes coming with Blockchain will be as large as the original invention of the internet, and this may not be overstated. Who would have imagined a decade ago that e-commerce, championed by Amazon and Alibaba will be displacing high street retailers, or that ride-hailing will be dominated by UBER, a technology platform?
There seems to be a seamless change happening in the Financial Sector. According to Anthony Jenkins, former CEO of Barclays, bank branch traffic has halved in the last five years, and bank profitability could collapse by 60% in the same period. A 2015 Goldman Sachs report estimated $4.7tn of financial services revenue was at risk of displacement from Fintech groups.
Regulators are now helping Fintechs
Fintechs are getting a lot of support from Regulators, believing that Fintech firms are small enough for any problems to be manageable, and on the other hand, might produce useful innovation (the sandbox approach). The intention is to lower market entry barriers for fintech companies. For instance, France’s Central Bank has announced opening up a new innovation lab, aiming to collaborate with blockchain startups.
In December 2015, Nasdaq executed its first trade on a blockchain, through its Linq ledger. The exchange said the blockchain promises to expedite trade clearing and settlement – all the steps needed to transfer the asset from seller to buyer including recording the transaction — from three days to as little as 10 minutes. That’s because the trades remove many manual processes and bypass third parties.
As such, “settlement risk exposure can be reduced by over 99%, dramatically lowering capital costs and systemic risk,”. Other stock exchanges tinkering with the blockchain include Australia, Germany, Japan, Korea, London, Toronto and Myanmar.
The Future of Fintechs
The future of Fintech seems bright. Accenture recently released a report which found that investment in Fintech around the world has increased dramatically from $930 million in 2008 to more than $12 billion by early 2015. Fintechs employ Artificial Intelligence, Big Data and Machine Learning to glean the credit habits of customers from their mobile usage, and so have mitigated against the risk of default.
The homepage of LendingClub (NYSE: LC) advertises personal loans of up to $40,000. You can “apply online in minutes” and “get funded in as little as a few days,”. Another prominent Fintech lender Funding Circle claims that small businesses can get loans from between $25,000 and $500,000 in as little as 10 days.
These are innovative services that seek to fill important niches in the credit markets. They enable people who have historically been shunned by banks to get loans in order to expand their businesses.
The lucrative Transfer market will be significantly impacted
The lucrative global transfers markets are major targets by Fintechs. International money transfers, which have long been a thorny issue, are getting easier. For smaller transactions, services like PayPal automatically convert currencies, so it’s easy for a customer to purchase goods from anywhere in the world.
More importantly, a service called TransferWise is streamlining international money transfers, significantly disrupting that sector by offering a 90 per cent discount on traditional bank transfer fees. According to the founder, Taavet Hinrikus, the idea was borne out of his personal frustration in money transfers. ‘It typically took 3-4 days to receive transfers, albeit the exchange rate used by banks was exorbitant, leading to a loss of almost 10% of the value of money sent’.
In this exorbitant regime, Western Union and HSBC typically earned $600m and $800m per annum respectively in profits from only transfers. These huge contributions to their bottom-line will be dearly missed when displaced by TransferWise and their co-travellers. In Taavet’s view, Fintechs will command about 40% of the global Financial Services market in the next 10 years.
Banks and Fintechs’ collaboration for mutual benefit
Fintech companies in emerging markets have shown that with blockchain technology, it is possible to leapfrog to new forms of banking.
Truth be told, Banks are best placed to continue to influence the future of Financial Services because of their huge branch network, solid reputations, and risk controls, as well as years of customer cultivation and loyalty. They, however, have to radically change the mindset of ‘we win when you lose’.
The big take away
The ubiquity of broadband and the pervasiveness of mobile phones, along with breakthrough technology such as Artificial intelligence, Big Data and Blockchain are expanding the frontiers for business models in ways that were hitherto not possible, and levelling the playing field in the process.
Any bank that does not read the signs and join the innovation train will definitely be disrupted and left behind. Remember that there was a time when the Post Office was at the centre of our lives. When was the last time you visited a post office?
Austin Okere is the Founder of CWG Plc, the largest security in the technology sector of the Nigerian Stock Exchange & Entrepreneur in Residence at CBS, New York. Austin also serves on the Advisory Board of the Global Business School Network, and on the World Economic Forum Global Agenda Council on Innovation and Intrapreneurship. Austin now runs the Ausso Leadership Academy focused on Business and Entrepreneurial Mentorship.

